Lightning
Brutal electrical phenomena, fascinating, dangerous and equally photogenic, lightning is widely appreciated by storm chasers.
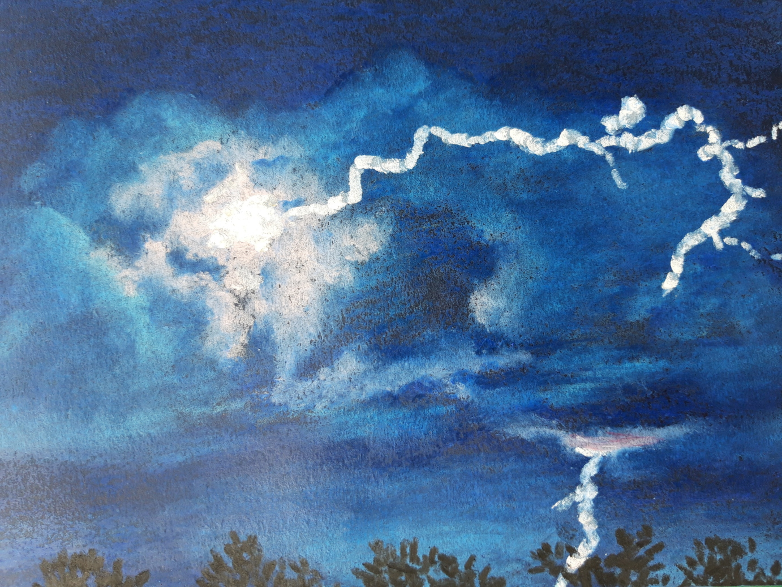

Lightning during a storm, oil pastel by Camille Risi from a free of rights photograph.
Specific features
The bolt of lightning is a visual phenomenon producing a bright zigzag that tears the sky. Like two peas in a pot, a lightning bolt always comes with thunder, a sound, a deafening cracking in the air.
Origin
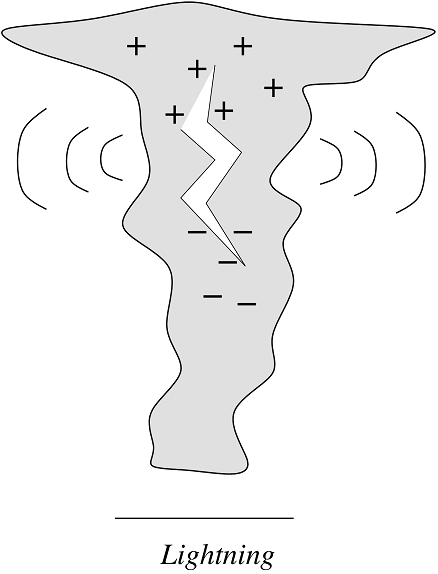 It all starts with a discharge of static electricity. In a cumulonimbus, ice crystals and droplets of water, carried around by violent updrafts and downdrafts, end up colliding. As they crash into each other, it strips away electrons from ice crystals that become positively charged, as electrons are negatively charged. These ice crystals rise up in altitude with their positive charge, because being lighter, it gets easier for them to stay in suspension. On the contrary, negative charges remain at the centre. This creates inside the cloud a difference in electrical charge, but it cannot keep on accumulating for ever. At some point comes the discharge, an electrical current that passes through these negative and positive areas. It heats the air at several dozens of thousands of degrees (it can reach 30 000°C, almost 6 times the temperature of our Sun!). The air becomes luminous, like the string of a lightbulb animated by an electric current, that’s the lightning bolt. In addition, the air heated so abruptly swells rapidly, creating a shock: this is the thunder. And light travels faster than sound, at 300 000 kilometres per second, whereas sound follows at only 340 metres per second. This is why we see lightning before we hear thunder. And the further away from the cloud you are, the more the sound falls late behind lightning. For instance, if you hear thunder only 3 seconds after seeing lightning, that means the discharge in the storm took place only 1 kilometre away from you. Time to get cover!
It all starts with a discharge of static electricity. In a cumulonimbus, ice crystals and droplets of water, carried around by violent updrafts and downdrafts, end up colliding. As they crash into each other, it strips away electrons from ice crystals that become positively charged, as electrons are negatively charged. These ice crystals rise up in altitude with their positive charge, because being lighter, it gets easier for them to stay in suspension. On the contrary, negative charges remain at the centre. This creates inside the cloud a difference in electrical charge, but it cannot keep on accumulating for ever. At some point comes the discharge, an electrical current that passes through these negative and positive areas. It heats the air at several dozens of thousands of degrees (it can reach 30 000°C, almost 6 times the temperature of our Sun!). The air becomes luminous, like the string of a lightbulb animated by an electric current, that’s the lightning bolt. In addition, the air heated so abruptly swells rapidly, creating a shock: this is the thunder. And light travels faster than sound, at 300 000 kilometres per second, whereas sound follows at only 340 metres per second. This is why we see lightning before we hear thunder. And the further away from the cloud you are, the more the sound falls late behind lightning. For instance, if you hear thunder only 3 seconds after seeing lightning, that means the discharge in the storm took place only 1 kilometre away from you. Time to get cover!
Evolution
Most bolts of lightning happen inside a cloud, but they can also link two clouds together, or a cloud and the air around it, or between a cloud and the surface. In the latter, lightning is highly dangerous to human beings who risk electrocution and it can also generate forest fires.
When to see it
The window to observe lightning is very short, you might miss it if you blink at the wrong time. But be reassured, you will have more than one occasion to catch one in a single storm. On average, the Earth is struck by lightning 100 times each second, you just need to be at the right place to see it.
Did you know?
It is possible that fires produced by lightning hitting the ground were the first source of fire for prehistoric women and men.






